In the dynamic world of international trade, recent developments between the European Union (EU) and China regarding electric vehicle (EV) tariffs have caught the attention of industry experts and consumers alike. The complexities surrounding this evolving relationship highlight not only economic considerations but also the broader context of global trade dynamics. The European Parliament's trade committee chair, Bernd Lange, recently remarked in an interview that the EU is nearing a resolution to eliminate tariffs on electric vehicles imported from China. His comments indicate a crucial pivot in the EU's approach towards the burgeoning market of Chinese electric cars. Lange explained that there might be strategic pricing from China, potentially leading to a scenario of “price distortion” in the EU market. This statement hints at the delicate balance the EU aims to strike between protecting local industries and fostering international trade.The recent history of EU tariffs on electric vehicles has been tumultuous. In October, the EU Commission officially voted to impose tariffs exceeding 35% on electric cars made in China. This significant rate stems from concerns about unfair competition fueled by Chinese government subsidies, which the EU argues provide manufacturers with an unfair advantage in the marketplace.The EU's rationale for this approach can be distilled into four main considerations. First, the issue of trade imbalance and subsidies is paramount. The EU believes that the substantial subsidies allotted to Chinese automotive manufacturers by the government undermine the competitive landscape within Europe. This has sparked a debate about what constitutes fair competition in a market that is increasingly driven by state intervention.Second, findings from investigations by the EU Commission indicated that the subsidies provided to Chinese manufacturers might harm the EU’s transition to electric vehicles, especially as European manufacturers adapt from traditional combustion engines. This sets the stage for a regulatory environment where the EU seeks to level the playing field through protective measures. Additionally, the EU’s automotive sector, which employs millions, is under pressure to adapt and compete. By imposing tariffs, the EU aims to safeguard its domestic industries while managing the rising popularity of electric vehicles from China. The increasing reliance on Chinese imports, particularly in terms of raw materials and component parts, has only complicated the trade deficit, and this has become a point of contention across member states.The reactions among EU member states have varied widely, illustrating the disunity within the bloc. For instance, countries like Germany and Sweden have expressed skepticism towards the proposed tariffs, fearing that they might harm local industries that rely heavily on the Chinese market. On the contrary, France supports tariffs, arguing that they will shield local jobs and manufacturers—especially in light of the concern that over-subsidized imports could flood the market and exacerbate unemployment.As the EU navigates these turbulent waters, it is also grappling with internal divisions regarding trade policy. Some stakeholders in China, particularly car manufacturers, also face the challenge of adapting to a potentially fragmented market where different tax strategies may influence competitive dynamics. For instance, companies like SAIC Motor and Geely have publicly stated their commitment to maintaining pricing strategies to counterbalance impending tariffs. The underlying tension is not merely economic; it reflects a broader geopolitical frisson between the EU and China against the backdrop of a shifting global trade order. Reports from institutions like the Kiel Institute for the World Economy indicate that a 20% tariff could lead to a substantial decrease in the volume of Chinese EV imports to the EU—an outcome that would significantly drive up vehicle costs for consumers.Furthermore, external factors are influencing the EU's tariff disposition. As the United States contemplates its own fiscal and regulatory landscape, the ripples of American policy decisions could reverberate across the Atlantic. The potential rollback of EV tax credits in the U.S., backed by influential automotive lobbying groups, introduces additional uncertainty into the market. Major players like Tesla, who already dominate the EV sector, will likely shift strategies to leverage any changes to their advantage. For the EU and China, the potential for collaboration exists if they choose to momentarily sideline their tariff disputes in favor of addressing shared challenges from the U.S.’s impending trade policy changes. As both regions increasingly recognize the significance of the electric vehicle market, they may find common ground—namely, the need to mitigate the effects of American trade policies on their respective automotive industries.Amid these complexities, some Chinese automakers are already diversifying their strategies to navigate the tumultuous terrain of EU tariffs. Companies like BYD have accelerated plans to establish production facilities in Europe to circumvent potential tariffs, while NIO is enhancing its local presence through research and product development centers. Such strategies underscore an adaptation mindset that is increasingly crucial for maintaining competitiveness in foreign markets.Through these rapidly evolving narratives, it’s apparent that while tariff negotiations and implications are significant, they are not isolated events. They are representative of broader geopolitical forces, market dynamics, and technological shifts that will continue to shape the contours of international trade for years to come. As both sides grapple with these complexities, the only certainty remains that tariffs will persist as a contentious issue—one requiring deft navigation from both policymakers and business leaders alike. Through a wider lens, the relationship between the EU and China in the context of electric vehicles is a microcosm of a much larger global trade dialogue. It showcases how intertwined the automotive industry has become across borders, how governmental policies can impact corporate strategies, and how rapidly the marketplace can shift in response to regulatory landscapes. As this situation continues to unfold, it will require vigilance, proactivity, and a deep understanding of both local and global markets to navigate the path forward.
Tariffs Never Sleep
📅
Published
Related Articles
Nvidia Surpasses Apple's Market Value
Oct-05, 2024


Weilai Loses, BYD Gains, Tesla Profits Big!
Aug-04, 2024

Is White Sugar More Sensational Than Gold Prices?
Sep-18, 2024

Trillion-Dollar Stimulus on the Horizon?
Nov-05, 2024

Is the Era of Large Models Reaching a Turning Point?
Sep-23, 2024

Tesla on the Edge of a Cliff
Aug-13, 2024

A-Shares Update: 13 Trillion Yuan Stimulus Unveiled
Oct-19, 2024

Factors Behind America's Strong Consumer Spending
Sep-30, 2024
Pre-Market Snapshot: Global Headlines
Jul-25, 2024

Nissan: A Downfall Awaited
Jul-06, 2024

Baido: The Potential Successor to Didi
Sep-28, 2024

Accelerated Inflow of Long-term Capital
Aug-29, 2024

New Monetary Policy Framework & Liquidity Traits
Dec-02, 2024

Ten Traits of Great Investors
Jul-12, 2024

Tariffs Never Sleep
Jul-28, 2024


Did the US raise interest rates from 5.25% to 5.5%?
Oct-11, 2024




Yinghua Fund Manager's Billions See Sharp Decline
Aug-31, 2024

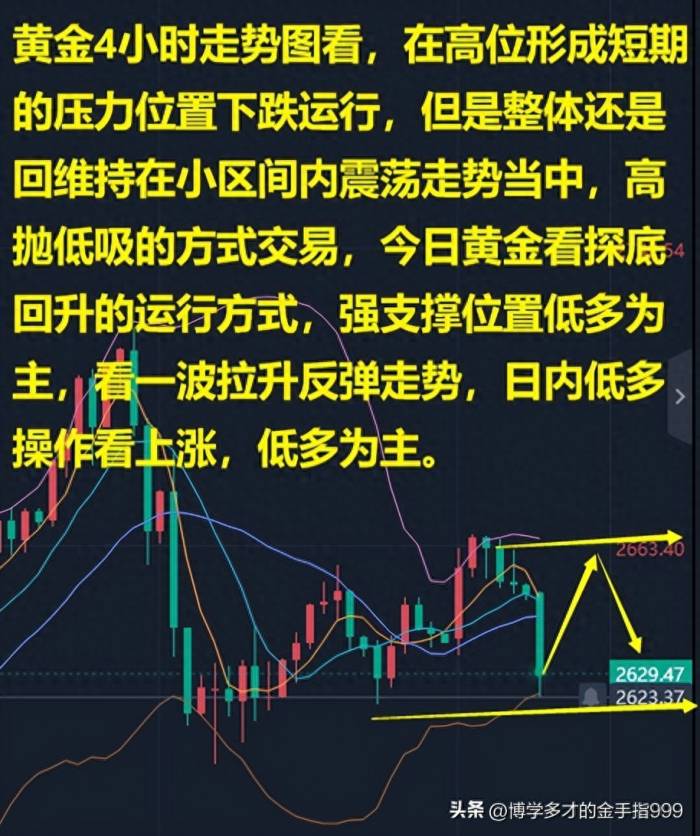
Gold and Silver: Bottoming Out for a Bullish Trend
Sep-13, 2024


High Prices Do Not Equal Spring
Jul-27, 2024

Semiconductor "Demon King" Sees $156.5 Billion Surge
Aug-03, 2024

Bond Bull Market Over at 2.80% 10-Year Yield?
Jul-20, 2024